Adding a Zim Server
Add a Zim Server to the network tree by right-clicking on the Zim Servers node and then clicking on Add Server…

Alternatively, a Zim Server node can also be added to the network tree by selecting Tools and then clicking on Add Server…

Next, enter the Zim Server‘s IP address in the field provided (default: localhost), the port number (default: 6002) and press OK

A new node containing the Zim Server‘s IP address will appear in the network tree. If Zim Server is running on the same machine as Zim Explore, the new node will be labeled localhost

Connecting to a Zim Server
To connect to the newly added Zim Server, right-click on the server node and click on Login
To complete the login procedure, enter the user name (default: ZIM), the password (default: “”) and click on OK

Once the connection to the server has been established, a + sign will appear beside the server node

The server node can be expanded by clicking on the + sign or by double-clicking on the server node itself

Removing a Zim Server
To remove a Zim Server node from the network tree, right-click on the server node and click on Remove

Zim Server Statistics
The Statistics utility displays relevant information pertaining to the configuration and state of the selected Zim Server.

The column headers in the Zim Server Statistics grid are described in the table below:
.
Browsing the Zim Server Configuration
The Zim Server Configuration utility displays and enables editing the contents of the zimconfig.srv configuration file for the selected Zim Server.
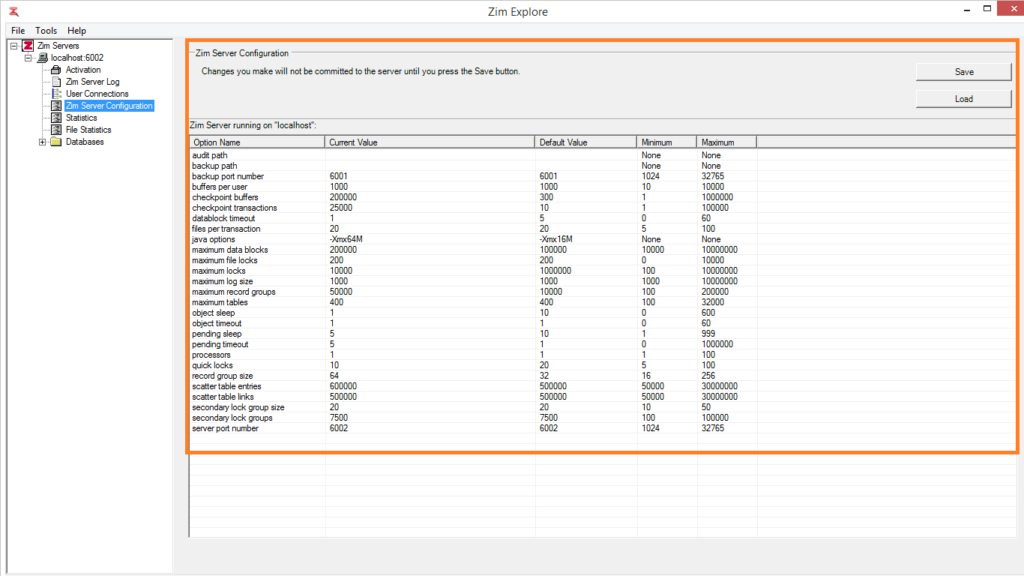
The column headers in the Zim Server Configuration grid are described in the table below:
| Column | Description |
|---|
| Option Name | The Zim Server configuration option |
| Current Value | The value assigned in the configuration file |
| Default Value | The default value for this option if no other value is assigned |
| Minimum | The minimum allowed value for this option |
| Maximum | The maximum allowed value for this option |
All the available Zim Server configuration options are listed in the table below. Click on any option to view more detailed information.
Editing the Zim Server Configuration
To change the value of a configuration option, click on the cell in the Current Value column along the row corresponding to the selected configuration option
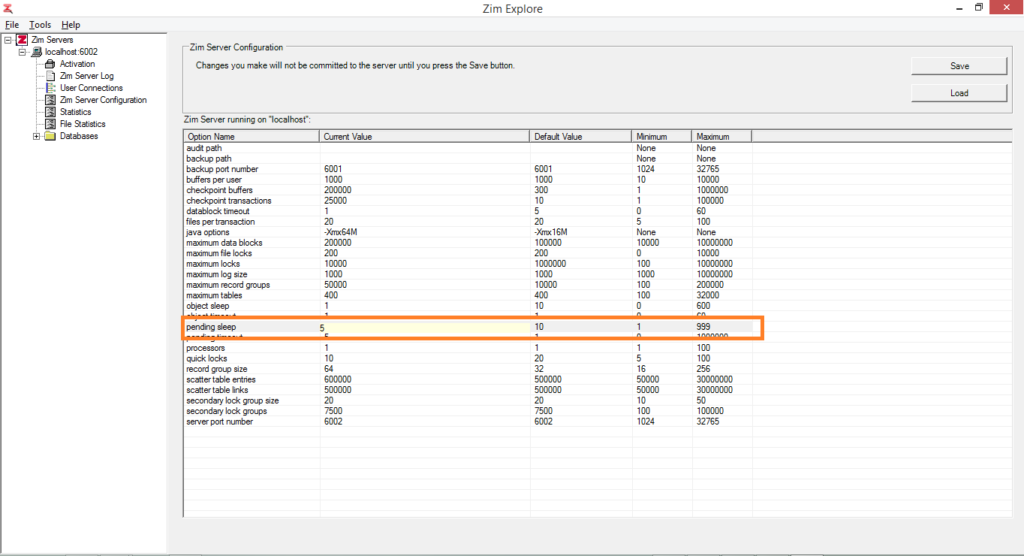
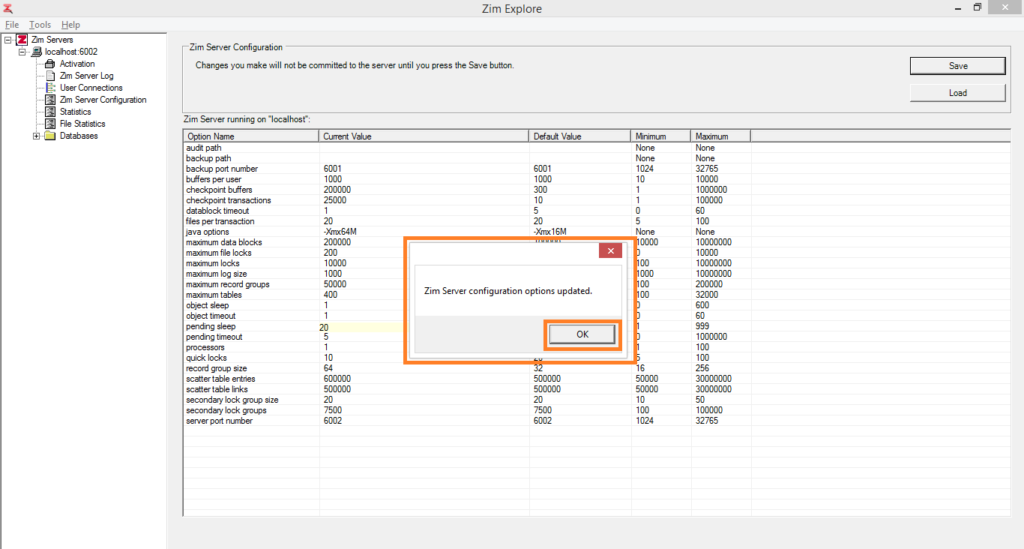
Type in or select the new value for the configuration option and click on Save to store the new configuration file

The Zim Server configuration changes have been accepted and will take effect as soon as Zim Server restarts. Click OK to dismiss the confirmation message
Browsing Objects by Type
The Object Browser provides a concise representation for database objects that belong to the selected database.
In the treeview, each database node has a child node labelled Objects, which in turn contains one child node for each object category.
Clicking on a particular category node will result in the Object Grid displaying only the database objects of the that category.
Each object occupies a single row and each of the object’s properties will be represented in a single column.


Object Categories
The table below lists all object categories that can be viewed in the Object Browser.
Also listed are the equivalent Zim:X commands that can be issued from a Zim:X client to retrieve the same objects.
To view more information about a specific object category, click on the category name in the left column.
Querying Databases
The Database Object Browser also provides an interface for issuing Zim commands to query the database.
For example, to list all the form fields belonging to the form fExample_Zim9, in the database, type the following Zim command in the entry field:
list all ffs where FormName = "fExample_Zim9"
… and press Go.
The form fields will be listed in the Database Explorer grid, where each form field will be represented in a single row and each of its attributes in a single column:

Note: List commands do not generate sets when issued from Zim Explore. If you wish to interact and manipulate objects, use ZXCLIENT or ZXCOMMAND.
Browsing the Zim Database Configuration
The Zim Database Configuration utility displays and enables editing the contents of the zimconfig.zim configuration file for the selected Zim database.
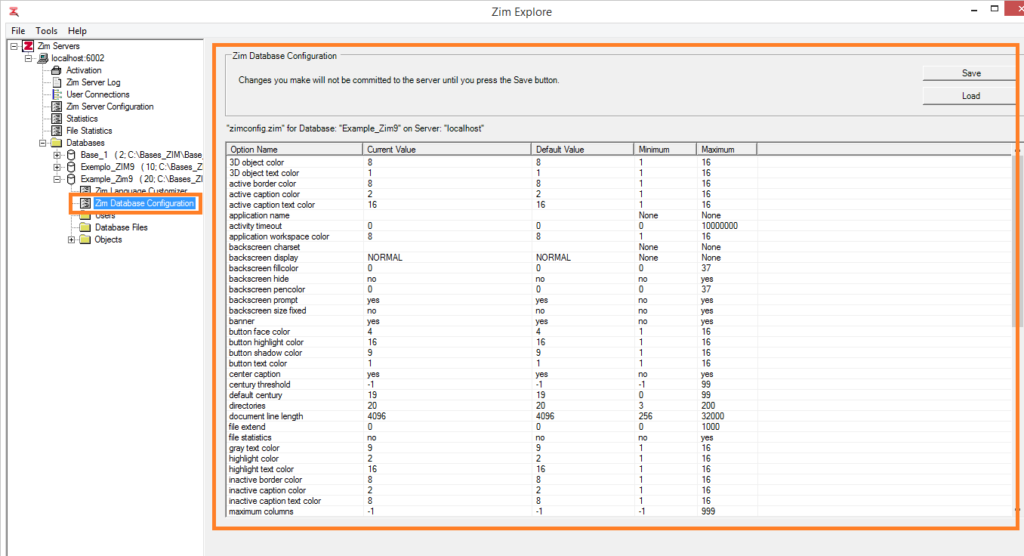
The column headers in the Zim Database Configuration grid are described in the table below:
| Column | Description |
|---|
| Option Name | The Zim database configuration option |
| Current Value | The value assigned in the configuration file |
| Default Value | The default value for this option if no other value is assigned |
| Minimum | The minimum allowed value for this option |
| Maximum | The maximum allowed value for this option |
.
The table below lists all the available Zim database configuration options. Click on any option to view more information about it.
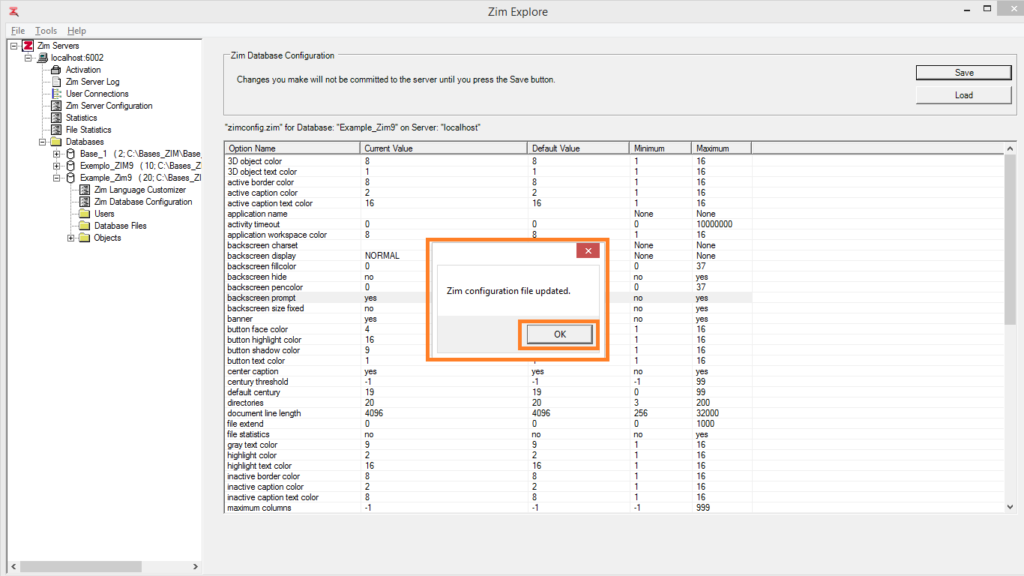
Editing the Zim Database Configuration
To change the value of a configuration option, click on the cell in the Current Value column along the row corresponding to the selected configuration option

Type in or select the new value for the configuration option and click on Save to store the new configuration file
The Zim database configuration changes have been accepted and will take effect as soon as Zim Server restarts.
The name of an application directory (Directories); otherwise, the one application directory in which the associated object may exist.
Valid Values
An 18-character string, containing a valid object name
Remarks
In Directories:
DirName is the name assigned to the directory.
In other Object Dictionary entity sets:
In any entity set, the principal object’s DirName must match the DirName of its owner.
If DirName is left blank, the object may exist in any number of application directories.
In DDDescriptions, DirName is where the object being described may be found.
In DisplayForms, DirName is where the owner-display of the associated form may be found.
See Also
ConstName, DDObjectName, DDOwnerName, DisplayName, DocName, EntName, FieldName, FormName, MenuName, OwnerName, RelName, RoleName, SetName, UserName, VarName
A constant is a programming object. Wherever the constant name is used in an application program, the software uses the value assigned to that constant in the Constants entity set.
Establishing a Constant
Call up the Zim IDE, select CONSTANTS from the DataBases menu, and use the tools of the Zim IDE Development to define the desired constant.
Creation of Constants step by step:





The value of the constant.
Valid Values
A character string or number (up to 256 alphanumeric characters).
The name assigned to a constant.
Valid Values
A valid object name.
See Also
DDObjectName, DDOwnerName, DirName, DisplayName, DocName, EntName, FieldName, FormName, MenuName, OwnerName, RelName, RoleName, SetName, UserName, VarName.
The data type of the constant’s value.
Valid Values
Char, varchar, alpha, varalpha, numeric, int, longint, vastint, or date
Remarks
If ConstType is $Null or blank, the data type of the constant is set to numeric when ConstValue is a number and to char in all other cases.
For more information about data types, consult your User’s Guide.
See Also
Decimals, Length, Type.


























